NAFLDsym™
 DILIsym Services, Inc. has significant expertise in the areas of drug-induced liver injury (DILI) and quantitative systems toxicology (QST) and has employed this expertise to develop and utilize the DILIsym® modeling software to evaluate the safety risk of numerous drug candidates. DSSI also has significant experience in the area of metabolic diseases and has leveraged this area of expertise to develop the new quantitative systems pharmacology (QSP) modeling software, NAFLDsym™ v1A. DILIsym Services, Inc. can now apply this new software to assist with clinical development in collaborative partnerships. NAFLDsym™ services include conducting simulations of compounds to evaluate and model their effects on key characteristics related to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
DILIsym Services, Inc. has significant expertise in the areas of drug-induced liver injury (DILI) and quantitative systems toxicology (QST) and has employed this expertise to develop and utilize the DILIsym® modeling software to evaluate the safety risk of numerous drug candidates. DSSI also has significant experience in the area of metabolic diseases and has leveraged this area of expertise to develop the new quantitative systems pharmacology (QSP) modeling software, NAFLDsym™ v1A. DILIsym Services, Inc. can now apply this new software to assist with clinical development in collaborative partnerships. NAFLDsym™ services include conducting simulations of compounds to evaluate and model their effects on key characteristics related to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is a prevalent, worldwide disease with few available treatment options. Accumulating lipids within the liver cause steatosis and impose lipotoxicity upon hepatocytes that can lead to declining liver function and ultimately liver transplant. Bringing effective treatments rapidly to market is paramount to improve patient health. QSP modeling has been demonstrated to accelerate clinical development, and we anticipate NAFLDsym™ will contribute to accelerating the clinical development of effective treatments for NAFLD patients.
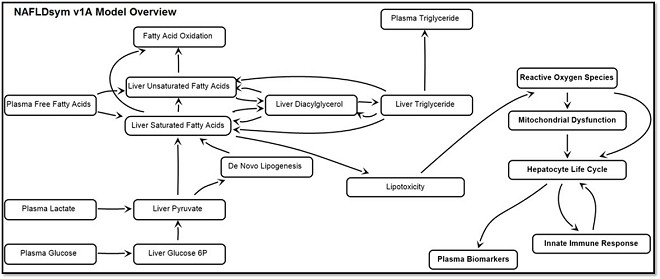
NAFLDsym™ v1A is a computational model of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and can be used to predict efficacy for treatment modalities developed for treating NAFLD. NAFLDsym™ v1A, includes many of the primary components of NAFLD pathophysiology such as:
- Steatosis
- Regulation of liver triglyceride and fatty acids
- Lipotoxicity
- Liver injury and proliferation
- Hepatocellular bioenergetics
- Innate immune system and inflammatory mediators
- Dynamic body weight and its effects on lipids
- Biomarkers (e.g., ALT, AST, cytokeratin cleaved K18)
These mechanistic components have been combined to generate >300 simulated NAFLD patients in NAFLDsym™ v1A. Reflecting the variability in clinical patient populations, these populations of simulated NAFLD patients (SimPops™) have a range of liver fat levels (steatosis), body weight, and many also have liver injury (e.g., elevated ALT).
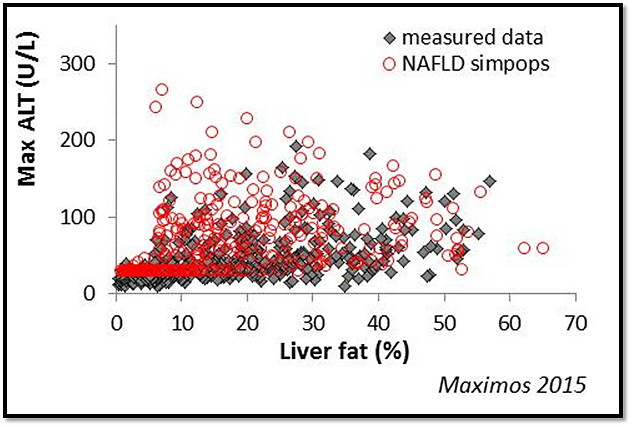
NAFLDsym™ has been used to evaluate several treatment modalities for NAFLD thus far, which included predictions of efficacy for each in the NAFLD SimPops™. NAFLDsym™ can be used to evaluate targets and/or specific compounds; the compounds can be simulated by utilizing key laboratory and/or clinical data describing DMPK and pharmacodynamic characteristics. These QSP approaches with NAFLDsym™ can enable pharmaceutical companies to prioritize compounds and targets. Additionally, NAFLDsym™ can be used to optimize clinical trial protocols by determining favorable dosing paradigms and outcome (i.e., liver fat reduction) measurement frequency.
DILIsym Services, Inc. is now working towards building upon the success with NAFLDsym™ v1A and expanding the capabilities in future versions to include pathophysiologic contributions from inflammation and fibrosis.